
- #Gparted live usb debian booting zip file#
- #Gparted live usb debian booting iso#
- #Gparted live usb debian booting download#
- #Gparted live usb debian booting windows#
You will need the GParted live iso file in this method. Just run the program on MS windows, then you can follow the GUI to create the live.
#Gparted live usb debian booting download#
Download Unetbootin to help you to create this Live USB flash drive.Choice 2 (Use GUI program on GNU/Linux):.(3) The partition must be on the cylinder boundary. (2) The partition must be marked as "bootable" in the partition table. If your USB flash drive or USB hard drive is not able to boot, check (1) Is there any partition in your flash drive ? It must contain 1 partition at least.Make sure you run it on newer GNU/Linux, e.g. (There is a known problem if you run makeboot.sh on Debian Etch, since the program utils/linux/syslinux does not work on that. WARNING! Executing it with wrong device name could cause your GNU/Linux not to boot. "cd /media/usb/utils/linux", then run "bash makeboot.sh /dev/sdd1" (replace /dev/sdd1 as your USB flash drive device name), and follow the prompts to finish that. To make your USB flash drive bootable, first change the working dir, e.g.Keep the directory architecture, for example, file "COPYING" should be in the USB flash drive or USB hard drive's top directory (e.g. Unzip all the files, and copy them into your USB flash drive or USB hard drive (You can make it by the command like: "unzip gparted-live-0.4.5-2.zip -d /media/usb/").If it's not automatically mounted, manually mount it by "mkdir -p /media/usb mount /dev/sdd1 /media/usb/". In this example, we assume /dev/sdd1 has FAT filesystem, and it is automatically mounted in dir /media/usb/. Let's say, for example, that you find it is /dev/sdd1. Next, run the command "dmesg" to query the device name of the USB flash drive or USB hard drive. Insert your USB flash drive or USB hard drive into the USB port on your Linux machine and wait a few seconds."mkfs.vfat -F 32 /dev/sdd1" WARNING! Executing it incorrectly could cause your GNU/Linux not to boot. gparted, fdisk, cfdisk or sfdisk) to create a partition with size 200 MB or more, Here we assume your USB flash drive or USB hard drive is /dev/sdd ( You have to comfirm your the device name, since it's _NOT_ always /dev/sdd) on your GNU/Linux, so the partition table is like: # fdisk -l /dev/sddĭisk /dev/sdd: 12.8 GB, 12884901888 bytesġ5 heads, 63 sectors/track, 26630 cylinders If the USB flash drive or USB hard drive does not have any partition, you can use disk tool (e.g. Prepare an USB flash drive or USB hard drive or external disk which has a partition using FAT (either FAT16, FAT32) file system.Extract files and make USB flash drive bootable under GNU/Linux.Therefore it's recommended to use the choice 1. The boot menu created by Unetbootin is not exactly the same boot menu as the one created in choice 1.

#Gparted live usb debian booting windows#
Executing it incorrectly could cause your MS windows not to boot. WARNING! Makeboot.bat must be run from your USB flash drive.
#Gparted live usb debian booting zip file#
Extract all the contents of the zip file to FAT16/FAT32 partition on your "flash drive." Keep the directory architecture, for example, file "COPYING" should be in the USB flash drive's top directory (e.g.If there is, you can use the existing one.

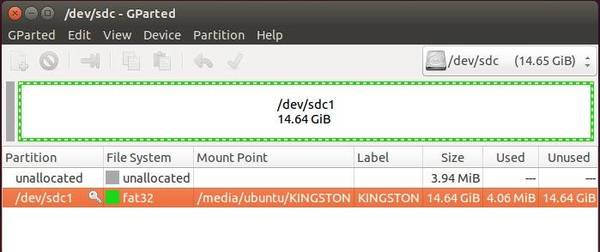
First, download GParted live iso or zip file.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
